Hillah, Iraq
Coordinates: 32.391761, 44.341330
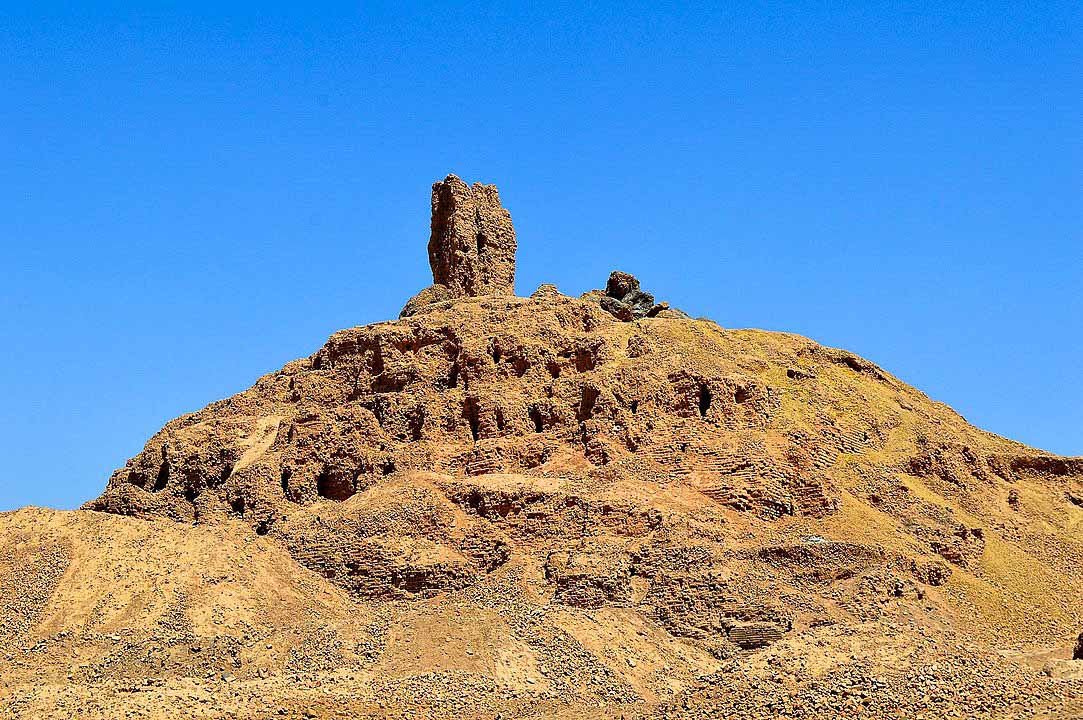
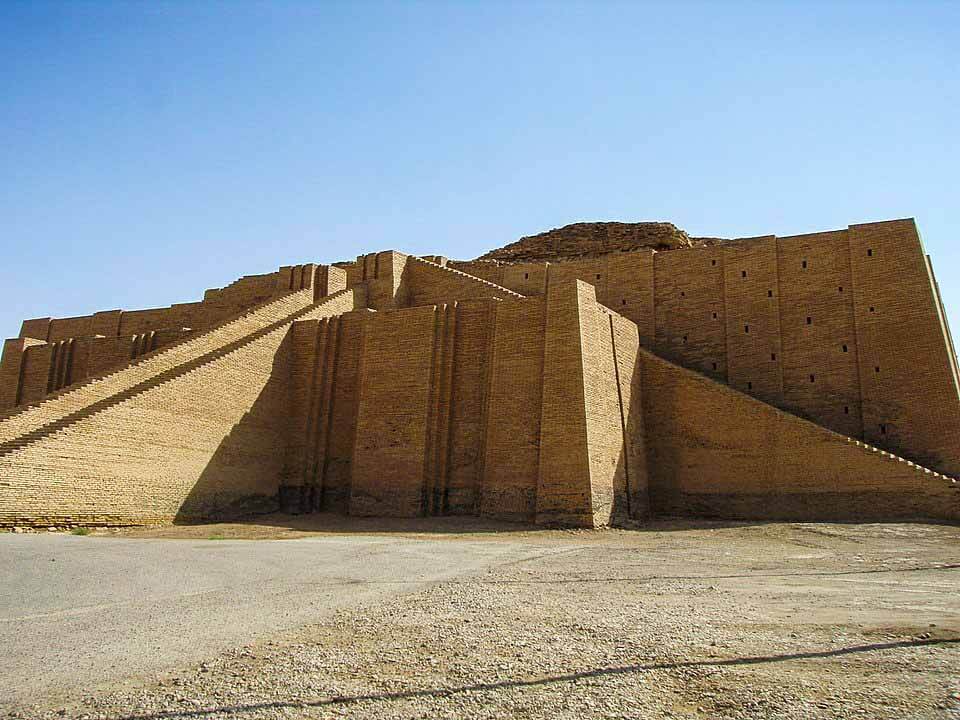
Borsippa or Birs Nimrud (having been identified with Nimrod) is an archeological site in Babylon Province, Iraq.
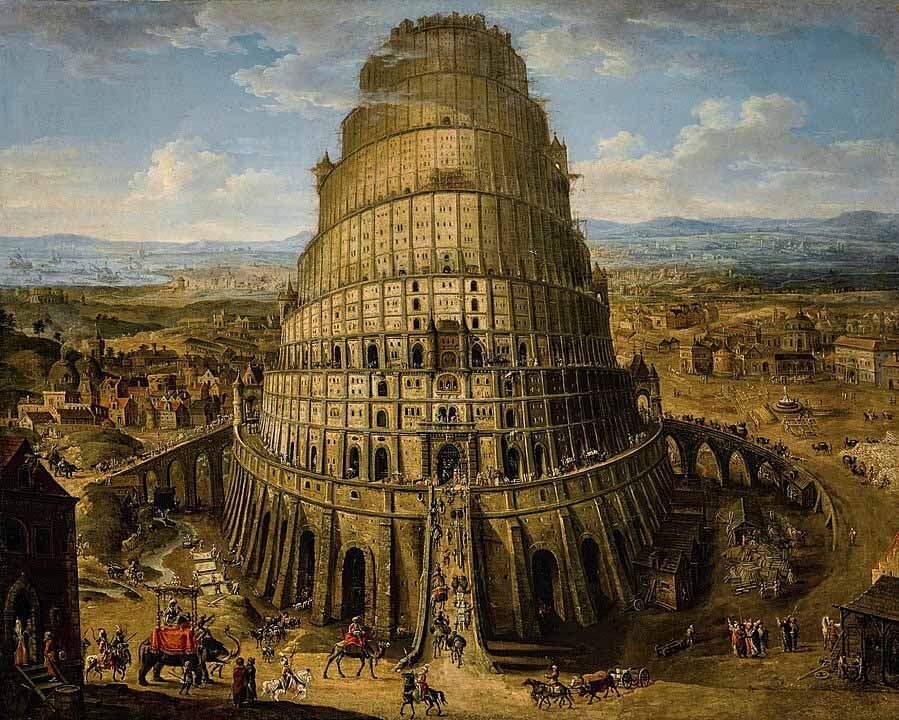
The ziggurat is today one of the most vividly identifiable surviving ones, identified in the later Talmudic and Arabic culture with the Tower of Babel.
However, modern scholarship concludes that the builders of the Ziggurat in reality erected it as a religious edifice in honour of the local false god Nabu, called the “son” of Babylon’s Marduk, as would be appropriate for Babylon’s lesser sister-city.
Borsippa was an important ancient city of Sumer, built on both sides of a lake about 17.7 km southwest of Babylon on the east bank of the Euphrates.
Borsippa is mentioned, usually in connection with Babylon, in texts from the Ur III period through the Seleucid period and even in early Islamic texts.
It was dependent upon Babylon and was never the seat of a regional power. From the 9th century BC, Borsippa was on the borderland south of which lay the tribal “houses” of Chaldea.
The temple to Nabu at Borsippa was destroyed in 484 BC during the suppression of a revolt against the Achaemenid king Xerxes.